The Shariah Screening Method for Stock investments can be quite confusing. In this post we will provide a clear concise breakdown on the most common Shariah principles applied to stock screening to help you make a better informed decision around your investments.
Disclaimer: The information in this article does not constitute any form of financial or investment advice by InvestingMuslim.com
We will work through a few examples to help you better understand how to apply widely accepted Shariah screening methodology based on the methods used by Shariah compliant advisors that advise the world’s largest index providers.
The Shariah screening methodology can be broken into two essential screening processes:
- Industry Based Shariah Screening: This is screening of the stock to ensure it is in a Shariah compliant sector, for example a company operating in the Tobacco industry would not be compliant.
- Accounting Based Shariah Screening: This method of screening focuses on compliance with Shariah accounting principles concerning cash reserves, debt, leverage and the share of revenue coming from non-compliant sources.
The Industry Based Shariah Screening method is fairly straight forward seeing as it relates to the industry a company operates in, which is something that is relatively easy to check and doesn’t require much effort.
On the other hand the Accounting Based Shariah Screening method requires going into a company’s financial statements and getting a better understanding of a company’s financial position from a Shariah perspective.
We’ll now go further in depth into the two essential Shariah screening processes along with a worked example to aid your understanding.
Industry Based Shariah Screening Methodology
The industry a company operates in will determine whether or not it passes the Shariah screening, it is widely accepted the below industries are deemed non-compliant with Shariah principles:
- Alcoholic Beverages ; companies involved in the manufacture, sale and distribution of alcoholic beverages.
- Gambling / Betting :companies providing gambling / betting services and/ or operating casinos.
- Pork: companies that derive their primary source of revenue from the production, sale and distribution of pork or pork derivative products.
- Tobacco: companies involved in the production, distribution and sale of tobacco and tobacco based products.
- Adult entertainment: companies involved in the production, sale and distribution of adult content.
- Advertising : companies involved in advertising activities and businesses not in compliance with Shariah and/or advertising means and methods which aren’t in compliance.
- Media & Entertainment: companies involved in the production, distribution and sale of entertainment content including music, films & TV shows. There are some exceptions including News, Education, Sports and Children’s content.
- Cloning
- Gold / Silver financing: Buying and selling of gold or silver as cash on a deferred basis.
- Banking and Financials: Banks, insurers etc involved in conventional finance involving interest, with the exception of Islamic financial institutions (banks, insurers, etc) that adhere to Shariah principles.
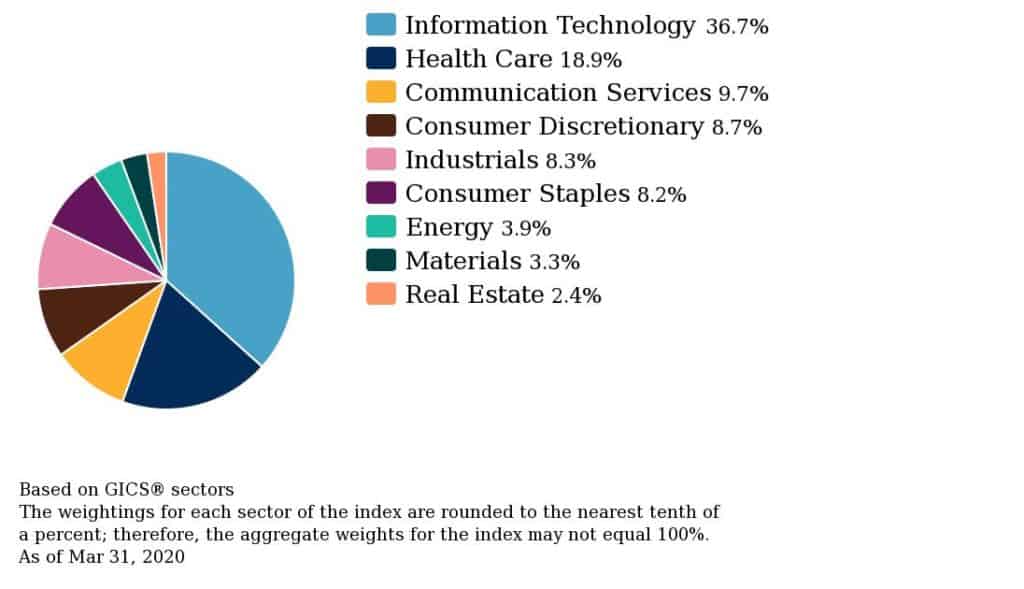
Note the S&P 500 Shariah Exclusions index includes a further industry restriction for companies involved in the manufacture, distribution and sale of weapons.
So that covers the main industry exclusions in the Shariah screening method.
Let’s run through an example to illustrate the Shariah Industry screening methodology, let’s take a major S&P 500 stock like Bank of America Corp (BAMC).
Bank of America Corp (BAMC) as the name would suggest is a major banking and financial corporation engaged in conventional interest based banking and as such this would exclude the corporation from passing the Industry Based Shariah Screening Methodology.
In contrast, Johnson & Johnson (JNJ) a major pharmaceutical, medical device and consumer goods company. As these industries pass the Industry Based Shariah Screening Methodology this stock would qualify the first stage of screening.
Let’s now move onto the next stage in the Shariah Screening Methodology, namely the Accounting Based Shariah Screening Methodology.
Accounting Based Shariah Screening Methodology
Once a company has qualified to pass the Industry Based Shariah Screening Methodology the next stage is reviewing the financial statements to ensure they comply with Accounting Based Shariah Screening.
To keep it simplified there are essentially three financial metrics we need to consider; a corporation’s debt position, cash and share of revenue attributed to non Shariah compliant activities.
It’s important to note here that unlike the industry a company operates in the financial position of a company can change more frequently hence it’s prudent to review the quarterly financial statements of a corporation you are evaluating or the latest annual statement to assess whether or not it passes the Accounting Based Shariah Screening Methodology.
The Accounting Based Shariah Screening Methodology focuses on the below financial ratio limits:
- Debt / Shareholder Equity must not exceed 33%
The Debt / Equity ratio is a measure of the financial leverage a company has taken on. Put simply it is a measure of how much debt as a proportion of shareholder funds is being used to fund operations. In particular it also reflects how well a company can finance it’s debt obligation with shareholder equity.
Once the leverage position is understood the next screen is the cash position:
- Accounts Receivables / Shareholder Equity < 49%
- Cash + Interest / Shareholder Equity < 33%
The Accounts Receivables / Shareholder Equity ratio provides an indication to how well a company’s cash position can cover account receivables and essentially how well shielded a company’s cash position is from a credit shock from it’s counterparties.
Finally with the leverage and cash position screened we need to consider the revenue coming from non-Shariah compliant activities (excluding interest)
- Non Shariah compliant income / Total Revenue < 5%
With all these calculations a 36 month average of the shareholder’s equity is used in these calculations.
That’s it, the two main methods used in screening stocks for Shariah compliance based on industry activity and the financial leverage position.